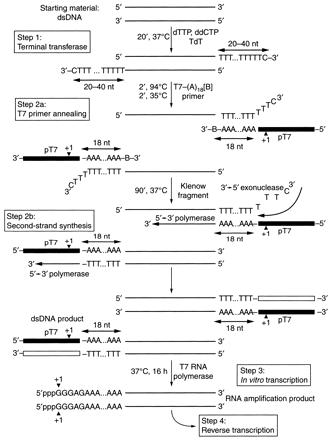
General strategy for the TLAD method. Starting with dsDNA template, TdT is used to add a poly(dT) tail to the 3′-ends of the template. This tail subsequently provides a conserved binding site for the annealing of T7 promoter (pT7)-poly(dA) primer adapters. Following subsequent second-strand synthesis using the large fragment of DNA polymerase I (Klenow fragment), one pair of dsDNA templates, with each pair member representing one of the two complementary strands of the dsDNA, is generated, with a T7 promoter at the 5′-end of the amplicon. In the subsequent IVT step, RNA is transcribed from this template in an isothermal reaction, producing an RNA amplification product consisting of both strands of the original dsDNA template in high microgram quantities. Note that each RNA strand will contain a short sequence from the T7 promoter and a poly(A) tract, 5′ relative to the amplicon. (Reprinted with permission from Liu et al. [2003].)










