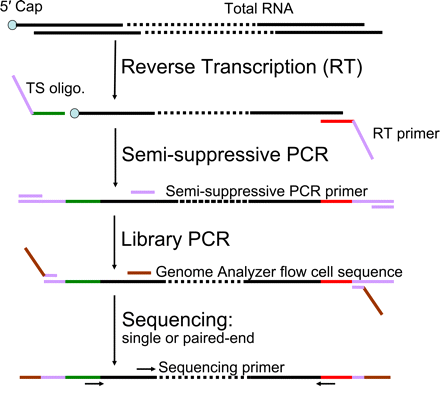
Flowchart of nanoCAGE protocol. Template-switching oligonucleotide (TS) and reverse transcription (RT) primer are added to the first-strand cDNA synthesis reaction. The three guanosine ribonucleosides at the 3′ end of the template-switching primer hybridize in a cap-dependent manner to cytidine deoxynucleosides added to the 3′ end of the newly synthesized cDNA strand by the reverse transcriptase (Hirzmann et al. 1993). After hybridization, the reverse transcriptase extends the cDNA strand using the template-switching oligonucleotide as a template. Hence, the cDNA originating from a capped RNA will have a 3′ end sequence reverse-complementary to the sequence of the template-switching oligonucleotide. These sequences are necessary to synthesize and amplify the second cDNA strand by semisuppressive PCR, which minimizes amplification of shorter artifacts (e.g., primer dimers or aberrant cDNAs template-switched from an RT primer or reverse-transcribed from a TS oligo). End sequences required for sequencing using a Genome AnalyzerIIx are introduced by “library PCR,” and the cDNAs are sequenced as single or paired ends.










