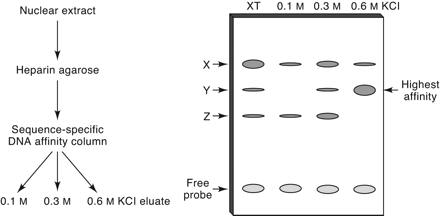
Comparison of protein–DNA interaction affinities in crude nuclear extracts by sequence-specific DNA affinity chromatography. Nuclear extracts from the murine T-cell line RLm11 were fractionated initially by heparin–agarose to remove nucleases. Sequence-specific DNA affinity chromatography was then performed using a resin with covalently linked oligonucleotides containing the D′ element from the Dntt promoter. The sample was applied to the column in a buffer containing 0.1 m KCl. Proteins were then eluted with 0.3 and 0.6 m KCl. Right, an idealized EMSA result is depicted; three protein–DNA complexes were detected when the extract was used (lane 1), but only one (complex Y) was retained on the column preferentially until the 0.6 m KCl elution (lane 4).










