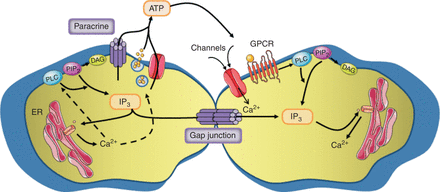
Mechanisms underlying the propagation of intercellular Ca2+ waves. Ca2+ waves can be propagated by the intercellular transfer of signaling molecules, such as IP3, through gap junctions. The extracellular pathway involves the release of different molecules, primarily ATP, via hemichannels, a vesicular pathway, or channels such as the P2X7 receptor. ATP diffuses to neighboring cells where it activates GPCRs or Ca2+-entry channels, thereby increasing [Ca2+]i. Regenerative mechanisms (activation of PLC or stimulation of ATP release mechanisms) are indicated by the dashed arrows.










