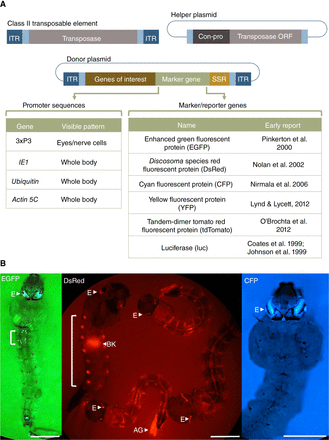
General organization and use of Class II transposable elements. (A) Schematic representations of a Class II transposable element and engineered helper and donor plasmids. Active Class II transposable elements have inverted terminal repeated (ITR) DNA sequences flanking a functional transposase gene complete with promoter and nontranscribed control DNA (Transposase). The helper plasmid (Helper) has the transposase open reading frame (ORF) under the control of a constitutive promoter (Con-pro). The donor plasmid (Donor) contains ITRs flanking genes of interest, a dominant marker gene along with control sequences to allow visible screening of transgenic animals, and in some cases sites for site-specific recombination (SSR). Both donor and helper DNA sequences are cloned into bacterial plasmids (thin lines) that allow production and purification for use in embryo microinjections or other DNA-introduction technologies. (Table) Examples of promoter sequences and marker/reporter genes along with early- or first-use citations in mosquitoes. (B) Examples of transposon-mediated transgenic mixed-instar Anopheles stephensi mosquito larvae marked with 3xP3-fluorescence genes. All larvae show transgene-mediated fluorescence in their eyes (E). Some larvae exhibit additional transgene-specific fluorescence in the segmented nervous tissue (vertical brackets), and anal gills (AG). The food bolus in the gut can produce background (BK) fluorescence. Horizontal bars, ∼1 mm. (EGFP) Enhanced green fluorescent protein, (CFP) cyan fluorescent protein, (DsRed) Discosoma species red fluorescent protein.










