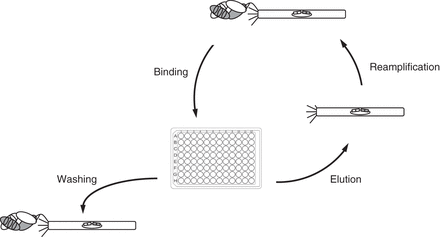
“Fragment antigen binding” (Fab)-phage library panning against immobilized antigen. Depicted is one round of panning that starts with adding a Fab-phage library to an antigen immobilized in one or more wells of a 96-well ELISA plate, for binding. Following stringent washing to remove nonspecific binders, specific binders are eluted using, for instance, trypsin (which removes the Fab phenotype but retains the Fab-encoding genotype) and then added to host bacterial cells for reamplification. Three to four rounds of panning are typically required to sufficiently enrich binders of high specificity and affinity from the Fab-phage library for identification by low-throughput screening. Screening methods using high-throughput sequencing only require one to two rounds of panning. Fab-phage libraries can also be selected against soluble antigen or on whole cells (see the text for details).










