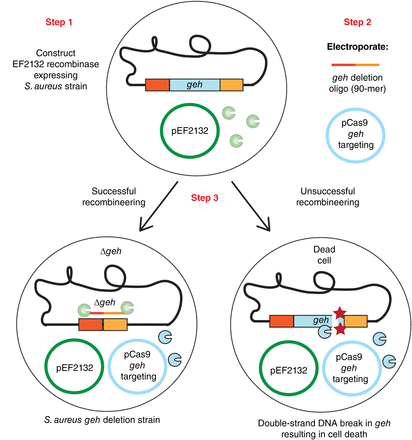
Schematic representation of the recombineering CRISPR–Cas9 counterselection method described in this collection to create gene deletions in Staphylococcus aureus. Step 1: An S. aureus strain containing plasmid pCN-EF2132tet (in the schematic, indicated as pEF2132) for expression of the Enterococcus faecalis recombinase EF2132 is constructed. Step 2: A 90-mer single-stranded DNA oligonucleotide containing sequences flanking the target gene (in this example, geh) is electroporated into the S. aureus strain from Step 1 alongside a CRISPR–Cas9 plasmid also targeting the target gene. Step 3: Upon successful recombineering using the oligonucleotide, a target-gene deletion strain is obtained (Δgeh in our example, left cell). If recombineering with the oligonucleotide does not take place, a Cas9-mediated double-strand break is introduced into the gene to be deleted, killing such bacteria with a wild-type allele of the gene (right cell).










